Hydroponics - Diseases
Root Rot

This problem is widespread, especially with cheap systems from the Internet and with beginners. Root rot usually has to do with insufficient oxygenation or an incorrect pH value.
Other causes:
Incorrectly placed air stones or insufficient
compressor performance in DWC systems (except Kratky).
Insufficient water movement and oxygenation in the system (except
Kratky).
The plants cannot develop aerial roots if they are planted
incorrectly.
The water temperature is too high (Maximum temperature should be
below 28°C).
The PH value is outside the guideline value of PH 5.5-6.5
Algae growth from exposure to light draws oxygen from the system.
Roots were not adequately cleaned prior to transfer to the system.
Common Remedies:
Clean the entire system and refill it.
Clean the roots well under running water.
System temperature during operation should be kept below 28°C.
PH value regulated between 5.5 - 6.5 and the EC value according to
the specifications.
Light entering the nutrient solution must be blocked to counteract
the growth of algae.
With a 3% hydrogen peroxide admixture with 6ml/L root rot can also
be minimized and prevented.
Micro and macro nutrient deficiencies

The most common deficiencies in hydroponic systems are magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium, iron and calcium deficiencies.
Magnesium deficiency:
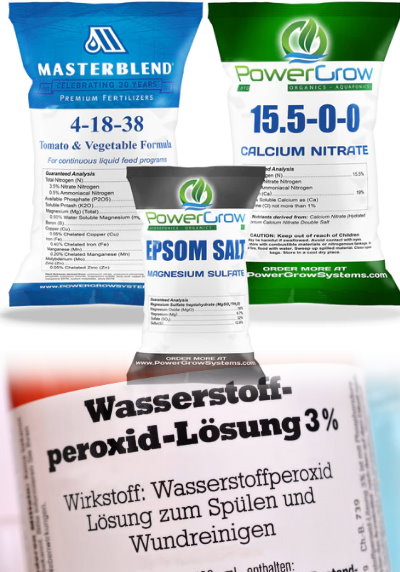
Magnesium is one of the most common deficiency problems in hydroponic systems. This can be remedied simply by adding Epson salt.
Mangan deficiency:
Manganese and iron are closely linked. If the iron content is too high, the absorption of manganese can be reduced. Manganese is an important trace element. It ensures strong cell walls, metabolism, the structure of the chloroplasts and photosynthesis. It inhibits photosynthesis which also slows growth. A disturbed root system, an iron content that is too high or a pH value that is too high can be the causes here.
Phosphorus deficiency:
Characteristic reddish to purple leaf discoloration
on older leaves, especially in leaf veins. The growth of the plant
and the development of roots is severely limited. The remedy is to
adapt the nutrient solution with a higher phosphorus content.
4-18-38 Tomato Masterblend has already proven itself worldwide on
a wide range of plant types.

Nitrogen deficiency:
Root rot and/or an incorrect PH value favor a
nitrogen deficiency.
Too low a temperature of the nutrient solution can also be
decisive here.
Pale yellow leaves are a clear sign of this.
A readjustment of the nutrient solution can help here.
Potassium deficiency:
With a lack of potassium, evaporation is reduced.
The result is that the temperature in the leaves rises and the
cells burn. This happens primarily at the leaf edges, where
evaporation is usually highest. Flowering is reduced and leafy
areas die off.
Potassium can also be added to the system....
Iron deficiency:
Manganese and iron are closely linked. (see
manganese deficiency)
A PH value above 6.5 can lead to iron deficiency.
Iron is supplied via the NPK nutrients in the form of
micronutrients.
In alternative DIY scenes, iron screws are often simply added to the tank to increase the iron content.
Calcium deficiency:
A very common problem which is very easy to solve.
Calcium deficiency usually manifests itself as localized
putrefaction of tissues and consequent stunted growth.
CalMag or calcium nitrate is commercially available and is a quick
fix.
Alternatively, you can boil eggshells, shred them and dissolve
them with strong vinegar.
Caterpillar Infestation

Affected leaves and visible caterpillars must be removed. Caterpillars should never be killed as they usually form beautiful butterflies.
Alternative spraying agents:
* Water - neem oil - biological dish soap or
dissolved curd soap.
* Chop the garlic and chillies, let stand for an hour mixed with
water, drain and mix with the spray water at a ratio of 1:10.
Garlic water, even mixed with raw onions, is a natural repellent. Even if the garden smells like a kebab shop for a while, the plants will thank you.
Other alternatives:
Leaves can be dusted with tobacco ash, algae lime or garlic powder.
Snails on visit

Snails are always annoying and a permanent work
site.
Hydroponic systems are usually less accessible. Due to the design
of these systems, however, electrical barriers are perfect
(self-adhesive metal strips which are supplied with a 9V battery
or low-voltage power pack).
Two or more strips are glued to the tank or pipe with a small
distance and supplied with a voltage. Voltages of 9V are
absolutely harmless to humans and pets.
Aphids

Arguably one of the worst invaders.
Aphids slowly kill the plants and are protected by ants. Here it
is usually necessary to act quickly. The ants can be reduced with
fly bands, but the lice usually only have a few natural enemies in
hydroponic systems.
Washing off with a strong jet of water is a first choice, but this
can sometimes cause damage to the plants.
A mixture of soft soap/potassium soap with water (15ml/1L) is a
good option for a weak infestation.
Alternative spraying agents:
* Water - neem oil (alternatively rapeseed oil) -
biological detergent or dissolved curd soap.
* Chop the garlic and onion, mix with water and allow to steep for
an hour, strain and mix with the spray water at a ratio of 1:10.
Fungal Infestation

Mold infestation in plants is usually promoted by
incorrect watering, too little air movement due to a lack of
trimming or poor choice of space, and too high humidity.
Alcohol, hydrogen peroxide or vinegar are suitable home remedies
for removing mold. Alcohol should be at least 70% concentration.
Medicinal alcohol or methylated spirits are well suited. The
hydrogen peroxide bleach should be bought in at least a 3%
solution. A mixing ratio of 1:3 with water spray is recommended
and should be repeated every 2-3 days.
For mixtures with alcohol or vinegar, adding ~35-50ml/L would be a
good choice.
Spider Mites

Spider mites or spider mites are easily recognizable
by their fine webs. Here it is important to act quickly.
They bite into plant leaves and suck out the succulent plant
fluids. In addition to the obvious damage it does to your plant,
it also makes it more susceptible to disease.
In addition to the usual household sprays (see aphids)
The following mixtures can be used here:
Vinegar based:
Mix 1/8 cup apple cider vinegar (white vinegar works too) with 1 cup water, 1/2 tsp baking soda, and a few drops of mild dish soap in a spray bottle.
Alcohol based:
Mixture of 1 cup rubbing alcohol and 4 cups water
and then spray the solution onto your plants. Cover the stems,
flowers and leaves thoroughly. Alcohol kills spider mites by
dehydrating them.
Mosquito Larvae

Sometimes small pests can also be found in the tank
and reservoir. This is often favored by a too high PH value.
The nutrient solution should usually be changed every 2-3 weeks or
refreshed via a circulation system. A filter in front of the pump
can remove quite a bit of floating pests.
If multiple systems are used, an elevated buffer tank with
circulation and filter stages is generally beneficial.
Addition of hydrogen peroxide (3-9%) not only supports root
growth, prevents mold growth, it is also helpful against
amphibious larvae and insects.
General Information
Main causes of infestation...
Plants are usually attacked by pests when they
already have a disease or deficiencies.
Regular monitoring of water & air temperature, nutrient
content (EC), PH value, lighting times, and adequate ventilation
are good companions in the fight against uninvited guests.
Growing plant species such as cucumbers, courgettes, tomatoes,
etc. should always be thinned out to ensure adequate
ventilation. Fans or regular ventilation for indoor systems are
also a good approach.
What to pay attention to?
Regularly changing the nutrient solution prevents many diseases and deficits. In the scene, a change every 2 weeks is recommended. However, this also depends on the plant density and growth stage. Large plants use more water than nutrients in hotter air temperatures. A water circulation with a buffer tank is recommended here to compensate for this. Flowering and bearing plant types require a different nutrient composition than lettuce. As a rule, 4-18-38 Tomato Masterblend has already proven itself worldwide for a wide range of plant types.
Addition of Epson salt and calcium nitrate/CalMag compensates for important deficits. Unfortunately, the cleaning of the systems used is often neglected. A small squirt of bleach or hydrogen peroxide in the cleaning water and a clean rag will get the job done quickly. For larger hydro farms, this work can also be done quickly with a high-pressure cleaner followed by an immersion bath.
How can you prevent it?
Many proven home remedies have already been discussed and these are also very suitable for prevention. Neem oil/rapeseed oil with some washing-up liquid/soap, hydrogen peroxide, garlic/onion broth and ash types also help preventively.
Various information can be found in the download area.