DIY Tips
NFT System

Probably the most common DIY system in hydroponics
is the NFT system. NFT stands for Nutrient Film Technique.
Holes are drilled into a round or rectangular PVC pipe with a hole
saw and a thin film of water supplies the roots. NFT pipes should
have a gradient of 3cm/m running length to ensure good drainage.
The holes are drilled with an electric drill to apply enough
power. As soon as the center drill has broken through the
material, the direction of rotation is switched to the left in
order to avoid fraying and damage to the drill hole.
NFT are also often built and sold with residual water. Reduction
sleeves are used at the end of the pipe to avoid problems in the
event of a power failure. Here, however, attention must be paid to
good oxygen enrichment.
Netcups in NFT-Systems
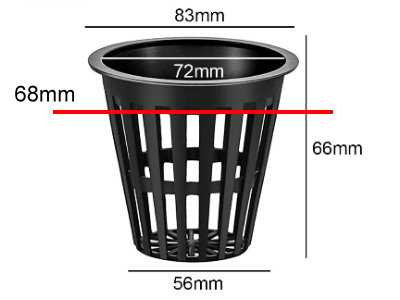
Net baskets are conical, which means there is a lot
of play due to the rounding of the tube.
If you have access to a CNC milling machine or want to do the work
with a jigsaw, you have to make the recesses oval.
First, a hole the size of the upper net basket is drilled in a
scrap piece and the net basket is inserted.
Now you measure the distance from the top edge of the net basket
to the height of the hole in the tube.
With this dimension, the diameter is now measured at this distance
on the net basket.
A standard net basket in a DM110mm tube results in an oval of
72x68mm which can be milled with a 3-axis CNC milling machine.
With a jigsaw, circles are printed out in the right size and glued
on.
Pumps und Tanks

Tanks:
This is where wisdom often diverges. When it comes
to tanks, the rule is always the bigger the better. On average,
you should calculate at least one liter per planting space. The
smaller the tank, the greater the pH fluctuations. The water
consumption of the plants must not be neglected either. Water is
used more than nutrients on hotter days.
It is also important to remember that the water must not get too
hot, otherwise the nutrient uptake is reduced and root rot is also
a consequence.
The tank is insulated, placed in a cool place if possible, or
buried.
Pumps:
Submersible pumps are usually used which are
switched either in continuous operation (NFT) or in cycles. The
lifting heights and conveying capacities usually do not correspond
to reality. It is best to calculate with at least one meter more
than the system needs and take the highest delivery rate in liters
here. Since the quality usually does not live up to what is
promised, you should always have a spare pump in stock.
DIY VGT

Some plastics contain halogens and must not be
burned. When forming VGT pockets, the heat gun must not be set too
hot. Patience is important here.
Combustion of PVC (polyvinyl chloride) when overheating can
produce dioxins, strong environmental toxins and carcinogens. In
addition, chlorine is released. Dissolved in water, it forms
hydrochloric acid, which among other things leads to chemical
burns in the respiratory tract.
PVC requires a temperature of 110-150°C for thermoforming. At a
temperature of 210°C, PVC begins to melt and toxic dioxins are
formed. It is generally advisable to carry out such work outdoors
or in a well-ventilated area.
Tip:
DIY VGT pipes are prone to water leakage and splashing. You can easily remedy this with inserted PVC rings. A DM50mm tube is cut into 20mm pieces and glued in place with glue or silicone. This reliably prevents water loss if this step has been carried out properly. To form the pocket, a piece of pipe is cut off at an angle.
PH-Value

The PH value is probably the most critical point in
a hydroponic system. Longer periods outside the recommended range
of PH 5.5-6.5 and root rot or diseases are the result.
There are many hacks to be found on the Internet, but they only
help to a limited extent.
Vinegar, citric acid, beer, urine, etc. quickly lower the pH
value, but it does not remain stable. After 1-2 days you are back
where you started. These biological alternatives do not contain a
PH buffer and are therefore only of temporal use.
To save yourself trouble, you should resort to professional means.
Aquaponics

If you want to do without chemicals entirely, you
can go the aquaponics route. This symbiosis forms between fish and
plants. Zander, catfish and talapia fish with a maximum density of
12-15 fish per m³ of water are very suitable.
It is important to have a well dimensioned filter system with
several stages.
Coarse and swirl filters use gravity and flow to filter out
solids. This can be drained via a drain tap and used as fertilizer
in the garden.
Fine filters are installed downstream before it goes into the
biofilter.
Biofilters contain a filter medium with a large surface area for
bacterial colonization. Ammonia is converted into nitrites in the
biofilter. Nitrification works best when dissolved oxygen levels
are high and organic matter (produced by uneaten fish food and
other waste) is low. Too much ammonia in the system is harmful to
plants and fish.
Compared to purely hydroponic systems, with an accelerated growth
rate, aquaponics can be compared to agricultural culture.
Algae infestation

Algae infestation can become a nuisance in
hydroponics. Warm water and nitrates as well as phosphates promote
algae growth. A good environment for this in hydroponic systems.
Insufficient water movement (e.g. Kratki, NFT with residual
watering or DWC) is also beneficial.
However, it also requires a sufficient amount of light to complete
the circle.
It is important to shield all water circuits and the tank from
light. Filter stages from the pumps also help to stop this.
All lines and systems are often painted black. this is a good
solution against the incidence of light, but everything heats up
in this way.
Reflective foils or self-adhesive aluminum metal strips, such as
those used for insulation in interior design, are better suited
here.
Two important points for outdoor systems!
Block light and heat as much as possible.
Automatisation

If you want things to run smoothly, then sooner or
later you won't be able to avoid automation.
PH sensors for Arduino are readily available and read out via BNC
and I²C.
EC sensors for conductivity and indicative of nutrient content are
constructed in a similar way.
With the hardware composition, however, it is important to ensure
that the EC sensor interferes with the PH sensor when both are
active.
The power supply must be switched on by code via relays for the
respective measurement.
Instructions for such projects can be found in sufficient numbers
on the Internet and are not explained in more detail here.
Planting

Here, too, every fan of hydroponics cooks his own
soup.
Usually net baskets (net cups) are used, which are available in
various sizes and are reusable.
If you want it cheaper then disposable plastic cups, pool noodles,
cut hard foam or rock wool can also be used.
With professional NFT systems, often only the stone wool cubes
with the young plants are placed directly in. Hard polystyrene
plates are used for rafting DWC. The only important thing is that
the plants have enough space to develop aerial roots and that
there is no waterlogging of the stem/stem to prevent rot. With
rigid foam, toothpicks or wooden skewers can provide additional
stabilization for larger plants.